Botox
Botox (Botulinum Toxin Type A) is a safe and thoroughly tested means of limiting a muscle’s ability to contract. This can result in both therapeutic and cosmetic benefits.
Therapeutic Botox or Pain Management Botox includes Temporomandibular Joint Pain commonly referred to as TMJ.
TMJ is the joint that acts as a hinge for your mouth. It’s what allows you to speak and chew. The muscles around the TMJ are very sensitive to stress and can tighten. Botox temporarily prevents nerve signals reaching your muscles and reduces abnormal muscle contractions to get the muscles to relax. It reduces the pain and restores movement to the mouth.
Another Therapeutic or Pain Management application of Botox is alleviation from Frontal and Temporal Headaches and Migraines. Botox has been FDA-approved for the treatment of chronic migraines since 2010. Injections of Botox prevent the transmission of pain signals between the brain and the nerves around the injection site. This significantly reduces the pain associated with headaches and migraines.
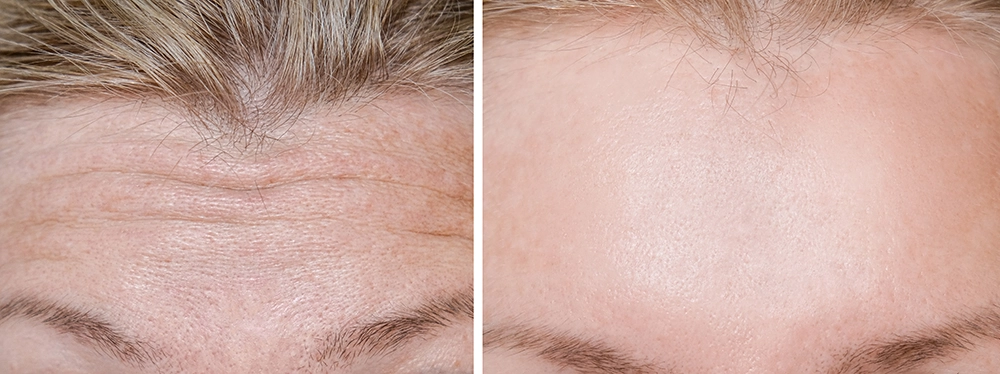
Cosmetic or *Dynamic Wrinkle Management is the use of Botox for facial rejuvenation. Your face gets a lot of use! You smile, frown, scowl and make a near infinite amount of expressions with your face. Wear and tear such as:
- Crow’s Feet
- Frown Lines
- Forehead lines
Are all symptoms from the facial muscles being used to make expressions. Over time, they lead to noticeable wrinkling on the face. Botox is used to seize the facial muscles from major contraction and make your face appear smoother and younger.
Dynamic VS Passive Wrinkles
Dynamic wrinkles are caused through the contraction of the muscles and disappear as the muscles relax. Passive wrinkles are present without muscle contraction.
While Botox does prevent dynamic wrinkles, Botox does not eliminate static wrinkles. It may however soften their appearance.